
 Settings
SettingsThe editorial team at ProProfs Quizzes consists of a select group of subject experts, trivia writers, and quiz masters who have authored over 10,000 quizzes taken by more than 100 million users. This team includes our in-house seasoned quiz moderators and subject matter experts. Our editorial experts, spread across the world, are rigorously trained using our comprehensive guidelines to ensure that you receive the highest quality quizzes.
Learn about Our Editorial Process | By Rodney.butler Rodney.butler Community Contributor Quizzes Created: 21 | Total Attempts: 27,579 Questions: 50 | Attempts: 3,179 | Updated: Sep 4, 2024
 Settings
Settings
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter Share on Whatsapp Share on Pinterest Share on Email Copy to Clipboard Embed on your website
It’s time for your finals! The Cisco Certified Network Associate programme has led you to this very moment, and it’s finally time to see if you’ve learned enough about routing protocols to secure yourself a noble career in the networking department. Let’s see how well you do! Good luck!
Questions and Answers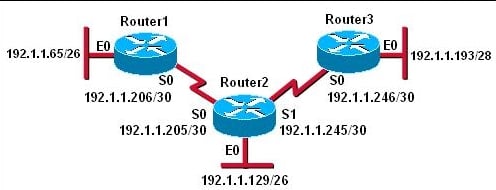
The address assigned to the Ethernet0 interface of Router1 is a broadcast address for that subnetwork.
The subnetwork configured on the serial link between Router1 and Router2 overlaps with the subnetwork assigned to Ethernet0 of Router3.
The subnetwork assigned to the Serial0 interface of Router1 is on a different subnetwork from the address for Serial0 of Router2.
The subnetwork assigned to Ethernet0 of Router2 overlaps with the subnetwork assigned to Ethernet0 of Router3.
Correct Answer
B. The subnetwork configured on the serial link between Router1 and Router2 overlaps with the subnetwork assigned to Ethernet0 of Router3.
Explanation
The problem with the addressing used in the topology is that the subnetwork configured on the serial link between Router1 and Router2 overlaps with the subnetwork assigned to Ethernet0 of Router3. This can cause routing issues as the routers may not be able to properly distinguish between the two subnetworks and route traffic accordingly.
Rate this question:
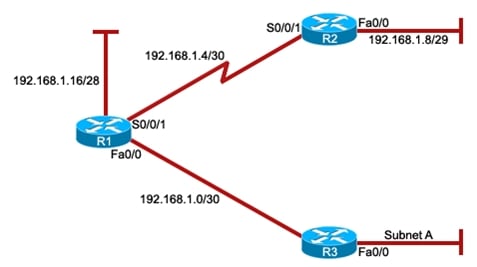
Explanation
The subnet 192.168.1.64/26 should be used for the new subnet. This subnet provides enough addresses for 50 hosts while wasting a minimum of addresses. The /26 subnet mask allows for 64 addresses, which is more than enough for the 50 hosts required. Additionally, using this subnet ensures that only the necessary number of addresses are allocated, minimizing wastage.
Rate this question:
Explanation
Routing loops can occur due to slow convergence, which is the time it takes for routers to update their routing tables after a change in the network topology. During this time, routers may still forward packets based on outdated information, leading to loops. Additionally, incorrectly configured static routes can also cause routing loops. If static routes are misconfigured, they may point to the wrong next hop or create circular paths, resulting in packets being continuously forwarded in a loop.
Rate this question:
Correct Answer(s)
A. It connects multiple IP networks.
C. It determines the best path to send packets.
Explanation
A router has two main functions. Firstly, it connects multiple IP networks by receiving packets from one network and forwarding them to another network. This allows different networks to communicate with each other. Secondly, a router determines the best path to send packets by analyzing the destination IP address and using routing protocols to find the most efficient route. By doing so, it ensures that packets reach their intended destination in the most optimal way possible.
Rate this question:
Correct Answer(s)
A. Tests Layer 2 connectivity
C. Enabled by default on each interface
E. Provides information on directly connected devices that have CDP enabled
Explanation
CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) is a proprietary Cisco protocol that operates at OSI layers 1 and 2. It is enabled by default on each interface and provides information on directly connected devices that have CDP enabled. CDP can be used to test Layer 2 connectivity between devices. However, it is not used for debugging Layer 4 connectivity issues.
Rate this question:
The router searches for a TFTP server if the startup configuration file is absent at the default location.
Correct Answer(s)
C. The bootstrap program searches for the startup configuration file in NVRAM.
E. The router searches for a TFTP server if the startup configuration file is absent at the default location.
Explanation
The first statement is true because the bootstrap program, which is a part of the router's firmware, searches for the startup configuration file in NVRAM (non-volatile random-access memory) during the boot process. This file contains the configuration settings for the router.
The fourth statement is also true because if the startup configuration file cannot be found in NVRAM, the router enters ROMMON (ROM Monitor) mode. In this mode, the router can be used to troubleshoot and recover from various issues.
Therefore, the correct answer is that the bootstrap program searches for the startup configuration file in NVRAM, and the router searches for a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server if the startup configuration file is absent at the default location.
Rate this question:
Explanation
When a router boots, it first looks for the Cisco IOS in the flash memory. If it doesn't find the IOS there, it then tries to locate it on a TFTP server. If the IOS is not found on the TFTP server, the router will finally look for it in ROM. Therefore, the default order to locate the Cisco IOS if there is no boot system command is flash, TFTP server, ROM.